transport system[3]
3:42 AM
today, i will move on to the second main component of the human circulatory system- blood vessels. Blood vessels are part of the circulatory system and function to transport blood throughout the body.
There are 4 types of blood vessels.
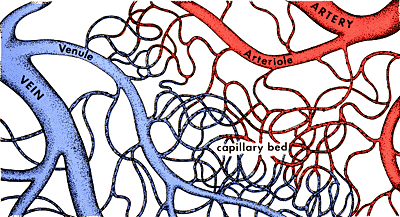
1. ArteriesArteries are elastic vessels that transport blood away from the heart. The largest artery of the body is the aorta. The aorta originates from the heart and branches out into smaller arteries. The smallest arteries are called arterioles which branch into capillaries.
 2. Veins
2. VeinsVeins are elastic vessels that transport blood to the heart. The smallest veins in the body are called venules. They receive blood from the arteries via the arterioles and capillaries. The venules branch into larger veins which eventually carry the blood to the largest veins in the body, the vena cava. The blood is then transported from the vena cava to the right atrium of the heart. The size of a vein is around 1 millimeter to 1-1.5 centimeters in diameter.

The artery and vein wall consists of three layers:
- tunica adventitia
The tunica adventitia is the strong outer covering of arteries and veins. It is composed of connective tissue as well as collagen and elastic fibers. These fibers allow the arteries and veins to stretch to prevent overexpansion due to the pressure that is exerted on the walls by blood flow.
- tunica media
The tunica media is the middle layer of the walls of arteries and veins. It is composed of smooth muscle and elastic fibers. This layer is thicker in arteries than in veins.
- tunica intima
The tunica intima is the inner layer of arteries and veins. In arteries this layer is composed of an elastic membrane lining and smooth endothelium that is covered by elastic tissues. Veins do not contain the elastic membrane lining that is found in arteries. In some veins the tunica intima layer also contains valves.
 3. Capillaries
3. CapillariesCapillaries are extremely small vessels located within the tissues of the body that transport blood from the arteries to the veins. Capillary walls are thin and are composed of endothelium (a single layer of overlapping flat cells). Oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients and wastes are exchanged through the thin walls of the capillaries.
The flow of blood is controlled by structures called precapillary sphincters. These structures are located between arterioles and capillaries and contain muscle fibers that allow them to contract. When the sphincters are open, blood flows freely to the capillary beds of body tissue. When the sphincters are closed, blood is not allowed to flow through the capillary beds.
Capillaries are so small that red blood cells can only travel through them in single file.
- 5-10 microns in diameter.
 4. Sinusoids
4. Sinusoids
The liver, spleen and bone marrow contain vessel structures called sinusoids instead of capillaries. Similar to capillaries sinusoids are composed of endothelium. The individual endothelial cells however do not overlap as in capillaries and are spread out. Oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, proteins and wastes are exchanged through the thin walls of the sinusoids. The size of a sinusoid is around 30-40 microns in diameter.
additional information:
Microcirculation deals with the flow of blood from arterioles to capillaries or sinusoids to venules. Blood flows freely between an arteriole and a venule through a vessel channel called a thoroughfare channel. Capillaries extend from this channel and structures called precapillary sphincters control the flow of blood between the arteriole and capillaries.
The precapillary sphincters contain muscle fibers that allow them to contract. When the sphincters are open, blood flows freely to the capillary beds where gases and waste can be exchanged with body tissue. When the sphincters are closed, blood is not allowed to flow through the capillary beds and must flow directly from the arteriole to the venule through the thoroughfare channel.
It is important to note that blood is supplied to all parts of the body at all times but all capillary beds do not contain blood at all times. Blood is diverted to the parts of the body that need it most at a particular time. For instance when you eat a meal blood is diverted from other parts of your body to the digestive tract.
Vessel Sizes (Diameter in Microns)
Arterioles
20-50
Capillaries
5-10
Sinusoids
30-40
Venules
30-40
Images courtesy of:
MedValetCarolina Biological Supply/Access Excellence





